The Relationship Between Kidneys and Blood Pressure

Did you know that your kidneys and blood pressure are closely linked? These two essential components of your body work hand in hand to maintain your overall health and well-being. In this article, we will explore the fascinating relationship between kidneys and blood pressure and understand how they affect each other.
Understanding the Role of Kidneys
Your kidneys are not just ordinary organs. They play a vital role in maintaining the balance of fluids, electrolytes, and waste products in your body. Acting as natural filters, they help remove excess water, toxins, and other waste materials from your blood, which are then eliminated through urine. But their job doesn't end there - kidneys also help regulate blood pressure.
Anatomy and Function of Kidneys
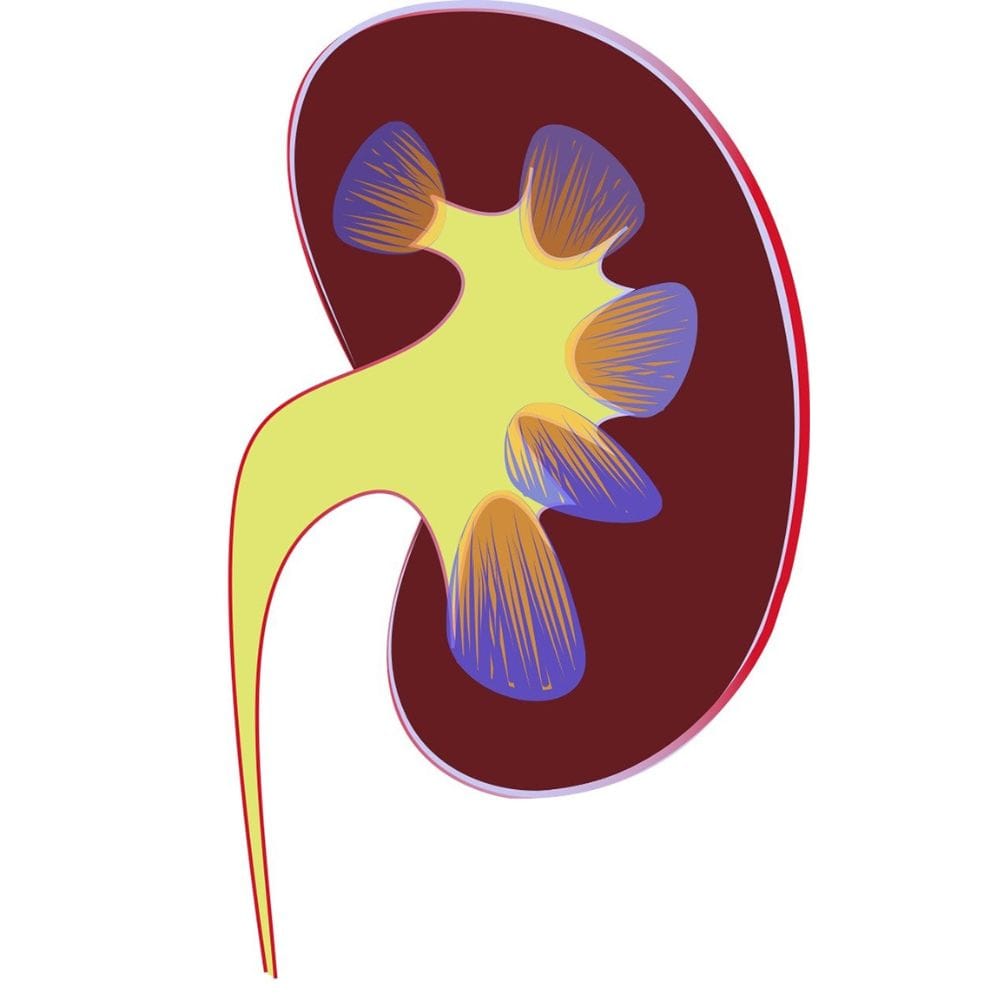
Let's start by exploring the incredible anatomy and function of your kidneys. Each person has two kidneys, shaped like beans and located in the upper part of the abdomen, on each side of the spine. Inside these small organs are millions of tiny structures called nephrons, responsible for filtering waste products and maintaining the balance of fluid and electrolytes.
The nephrons work by filtering blood and separating waste materials from valuable substances like water, minerals, and salts. This filtration process results in the formation of urine, which then travels through the ureter to the bladder for eventual elimination from the body.
But did you know that the kidneys are also involved in the production of a hormone called erythropoietin? This hormone stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow, ensuring that your body has enough oxygen-carrying cells to function optimally. Without the kidneys, this crucial hormone would not be produced, leading to a decrease in red blood cell production and potentially causing anemia.
How Kidneys Regulate Body Fluids
One of the most critical roles of your kidneys is to maintain the right balance of fluids in your body. They do this by adjusting the volume of urine produced, depending on the body's needs.
When you're dehydrated, your kidneys conserve water, producing less urine to prevent further fluid loss. Conversely, when you're adequately hydrated, your kidneys excrete excess water, ensuring your body doesn't retain more fluid than necessary.
But did you know that the kidneys also play a role in regulating the concentration of electrolytes in your body? Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, are essential for various bodily functions, including nerve and muscle function. The kidneys carefully monitor and adjust the levels of these electrolytes, ensuring they remain within a narrow range. This delicate balance is crucial for maintaining proper cellular function and overall health.
The Importance of Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force exerted by your blood against the walls of your arteries as it circulates throughout your body. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is crucial for the proper functioning of your vital organs and overall well-being.
When your blood pressure is within a normal range, your heart doesn't have to work as hard to pump blood, reducing the strain on your cardiovascular system. This helps to prevent conditions like heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage, which are often associated with high blood pressure.
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is measured in two numbers: the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure represents the force when the heart contracts, pumping blood into the arteries. The diastolic pressure, on the other hand, reflects the force when the heart relaxes between beats.
It's important to understand that blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day in response to activities, emotions, and even the time of day. Factors like stress, caffeine intake, and physical exertion can all influence your blood pressure readings.
The Effects of High and Low Blood Pressure
Both high and low blood pressure can have detrimental effects on your health if left unmanaged.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can damage the arteries over time, leading to an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. On the other hand, low blood pressure, or hypotension, may cause dizziness, fainting, and inadequate blood flow to vital organs.
It's essential to monitor your blood pressure regularly and make lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and staying physically active, to keep it within a healthy range. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help you develop a personalized plan to manage your blood pressure and reduce the risk of associated health complications.
The Connection Between Kidneys and Blood Pressure
Now that we understand the individual roles of kidneys and blood pressure, it's time to unveil their intricate connection and how they influence each other.
Understanding the relationship between kidneys and blood pressure is crucial for maintaining overall health. The kidneys, often referred to as the body's filtration system, play a significant role in regulating blood pressure. This intricate process involves a delicate balance of hormones and physiological mechanisms that work together to ensure blood pressure remains within a healthy range.
Kidneys' Influence on Blood Pressure
Your kidneys significantly regulate blood pressure through a complex process involving hormones and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. When blood pressure drops, your kidneys release an enzyme called renin, which triggers a series of events resulting in the production of a hormone called angiotensin II. This hormone constricts blood vessels and signals the release of aldosterone, which promotes sodium reabsorption and water retention, ultimately increasing blood pressure.
Moreover, the kidneys also help regulate blood pressure by controlling the volume of blood in the body. By adjusting the amount of water and sodium excreted in the urine, the kidneys can influence blood volume and, consequently, blood pressure. This intricate dance between the kidneys and blood pressure highlights the sophisticated mechanisms at play in maintaining cardiovascular health.
Blood Pressure's Impact on Kidney Health
Conversely, uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage the delicate blood vessels in your kidneys, known as nephrons. As a result, your kidneys may lose their ability to filter blood efficiently, leading to a condition called chronic kidney disease. This underscores the crucial importance of keeping your blood pressure within a healthy range to protect your kidneys from potential harm.
Chronic kidney disease, often associated with hypertension, can progress silently over time, highlighting the insidious nature of uncontrolled high blood pressure. The damage caused to the nephrons by persistent elevated blood pressure can have far-reaching consequences on kidney function and overall health. Therefore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, is essential in safeguarding both kidney function and blood pressure levels.
Common Kidney and Blood Pressure Disorders
Several disorders are directly related to the intricate relationship between kidneys and blood pressure. Let's take a closer look at two of the most common conditions:
Hypertension and Kidney Disease
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease. The sustained elevated pressure can damage the blood vessels in and around the kidneys, gradually impairing their function over time.
It is essential to manage hypertension effectively to prevent further damage to the kidneys. Lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet low in sodium, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can help control blood pressure levels. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to manage hypertension and protect kidney function.
Chronic Kidney Disease and Blood Pressure
On the other hand, chronic kidney disease can also contribute to high blood pressure. Damaged kidneys may not effectively remove excess fluid and waste from the body, leading to fluid retention and increased blood pressure.
Individuals with chronic kidney disease are often advised to monitor their blood pressure regularly. Maintaining a stable blood pressure is crucial in slowing down the progression of kidney damage. Healthcare providers may recommend specific blood pressure targets and medications to help manage blood pressure in individuals with chronic kidney disease.
Prevention and Management
Fortunately, there are proactive measures you can take to maintain healthy kidneys and blood pressure. Let's explore some lifestyle changes and medical interventions:
Lifestyle Changes for Healthy Kidneys and Blood Pressure
1. Maintain a balanced diet that includes low-sodium, high-fiber foods, fruits, and vegetables.
2. Exercise regularly to promote circulation and reduce the risk of high blood pressure.
3. Limit alcohol consumption and avoid smoking, as these habits can adversely affect kidney function and increase blood pressure.
4. Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies.
5. Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Proper hydration is essential for kidney function and maintaining blood pressure.
6. Get enough sleep to support overall health and well-being. Lack of sleep can contribute to high blood pressure and negatively impact kidney function.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient. In such instances, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications specifically aimed at controlling blood pressure and protecting kidney function. It's important to work closely with your healthcare team to find the most appropriate treatment plan for you.
7. Regularly monitor your blood pressure at home using a reliable blood pressure monitor. This can help you and your healthcare provider track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
8. Consider alternative therapies such as acupuncture or herbal supplements, under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. These approaches may complement conventional treatments and support kidney health.
9. If you have underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or hypertension, it is crucial to manage them effectively. Properly controlling these conditions can help prevent kidney damage and maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
10. Attend regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to assess your kidney function and blood pressure. Early detection of any potential issues can lead to timely interventions and better outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate relationship between kidneys and blood pressure is vital for maintaining your overall health and well-being. By taking proactive steps to keep your blood pressure within a healthy range and caring for your kidneys, you can ensure their optimal function and prevent potential complications. Remember, your kidneys and blood pressure are health partners, and nurturing their relationship is key to a vibrant life.
Thanks for reading.
BestPharmaReviews.



