Modern Methods for Treatment of Infertility

Infertility is a complex and challenging issue that affects many couples worldwide. The advancements in medical science have paved the way for a myriad of treatment options, catering to the diverse needs of individuals experiencing difficulties in conceiving. This article aims to elucidate the modern methods of infertility treatment, focusing on understanding its causes, hormonal treatments, assisted reproductive technologies, and surgical interventions.
Understanding Infertility: Causes and Diagnosis
Infertility is characterized by the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse. Various factors contribute to infertility, making a comprehensive understanding essential for diagnosis and treatment. Identifying the underlying causes is the first step in addressing the condition effectively.
The Role of Age and Lifestyle in Infertility
The age of individuals trying to conceive plays a significant role in fertility. Women’s fertility typically declines after age 30, with a more pronounced decrease after age 35. Similarly, men's fertility may be affected negatively as they age, although the decline is less dramatic than in women.
Lifestyle choices further influence fertility. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity can all hinder reproductive health. Addressing these lifestyle issues can significantly enhance the chances of conception. For instance, maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can improve overall reproductive function. Regular physical activity helps manage weight and boosts hormonal balance, which is crucial for both male and female fertility.
Common Medical Conditions Leading to Infertility
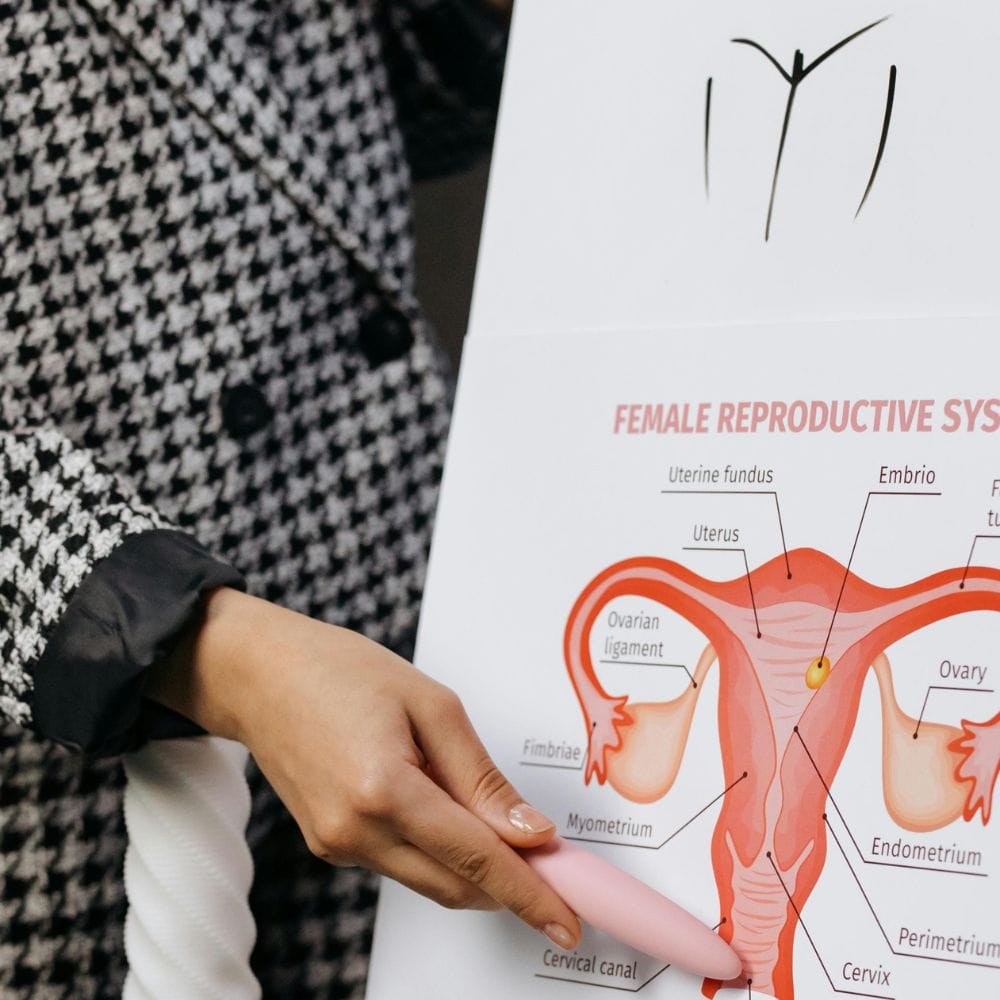
Several medical conditions can inhibit fertility in both men and women. For women, conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and irregular ovulation are significant contributors. In men, low sperm count, hormonal imbalances, and certain genetic disorders can lead to infertility.
Additionally, chronic illnesses like diabetes, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases can complicate fertility issues, often requiring specialized treatment plans to manage both the condition and its reproductive implications. It is also worth noting that certain infections, such as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can lead to scarring or blockages in the reproductive tract, further complicating the ability to conceive. Regular screenings and prompt treatment of infections can help mitigate these risks.
Diagnostic Tests for Infertility
When couples face infertility, healthcare providers may recommend a series of diagnostic tests to identify any underlying issues. In women, these tests often include blood tests to check hormone levels, imaging studies such as ultrasound to examine reproductive organs, and a hysterosalpingogram to assess the fallopian tubes.
For men, semen analysis is crucial, assessing sperm count, motility, and morphology, which can provide insights into male fertility health. Only through these diagnostic tests can healthcare providers tailor appropriate treatment plans effectively. Additionally, genetic testing may be recommended in certain cases to identify chromosomal abnormalities that could impact fertility. Understanding the results of these tests is vital, as they can guide couples toward the most suitable interventions, whether that be lifestyle modifications, medications, or assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Hormonal Treatments for Infertility
Hormonal treatments play a prominent role in addressing specific infertility issues, particularly those related to hormonal imbalances. These treatments aim to restore normal hormone levels and regulate ovulation in women and enhance sperm production in men.
Understanding Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can occur due to various factors, including age, stress, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions. For women, irregular levels of hormones such as progesterone and estrogen can disrupt the menstrual cycle and impair ovulation, making it difficult to conceive. For men, low testosterone levels can lead to decreased libido and sperm production.
Recognizing these imbalances is essential for selecting the most appropriate treatment. Simple lifestyle changes, medication, or more advanced clinical procedures may be prescribed based on individual needs. Factors such as body weight, diet, and exercise can significantly influence hormone levels. For instance, maintaining a healthy weight can help regulate menstrual cycles in women, while regular physical activity can boost testosterone levels in men, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach to fertility.
Types of Hormonal Treatments
Hormonal treatments for infertility typically include medications that stimulate ovulation or regulate hormonal levels in both men and women. Clomiphene citrate is a common medication prescribed to women to induce ovulation.
In cases where hormonal supplementation is necessary, women may receive injections of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or gonadotropins to trigger ovulation. For male infertility, testosterone replacement therapy may be utilized to restore hormone levels and improve sperm production. Additionally, other medications like letrozole, which is often used in breast cancer treatment, have shown promise in inducing ovulation in women who do not respond to clomiphene citrate. This expanding array of treatment options underscores the importance of personalized care in addressing infertility.
Success Rates and Side Effects of Hormonal Treatments
Success rates of hormonal treatments vary depending on the individual and the specific causes of infertility. Generally, women undergoing ovulation induction treatments can expect a success rate of 30-50% per cycle, depending on age and health conditions.
While hormonal treatments can be effective, potential side effects should also be considered. Women might experience mood swings, headaches, or bloating, while men undergoing testosterone therapy may face risks such as increased estrogen levels or a reduction in sperm production if not monitored closely. Moreover, some women may develop ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a condition that can occur when the ovaries are overstimulated, leading to swollen and painful ovaries. It is crucial for patients to have open discussions with their healthcare providers about the risks and benefits of hormonal treatments, ensuring they are well-informed and supported throughout their fertility journey.
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
Assisted Reproductive Technology refers to a range of medical procedures aimed at addressing infertility. ART can be an effective option when traditional methods fail to result in conception. As society becomes increasingly aware of reproductive health issues, ART has gained prominence, offering hope to countless couples who face challenges in starting or expanding their families.
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is one of the most widely recognized ART procedures. It involves retrieving eggs from a woman's ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory setting, and then implanting the embryo back into the woman’s uterus. IVF success rates vary depending on factors such as age, the cause of infertility, and overall health, but many couples find it a viable option for conception. The process can be emotionally taxing, requiring couples to navigate the complexities of hormone treatments, egg retrieval, and embryo transfer, but the potential for success often outweighs these challenges.
IVF also has room for customization; for instance, preimplantation genetic testing can be performed to screen for genetic disorders before embryo transfer, offering peace of mind for couples concerned about hereditary conditions. Additionally, advancements in cryopreservation allow for the freezing of embryos, providing flexibility for couples who may wish to delay implantation for personal or medical reasons. This technology not only enhances the chances of a successful pregnancy but also empowers couples to make informed decisions about their reproductive futures.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) is a specialized form of IVF where a single sperm is directly injected into an egg. This technique improves the chances of fertilization and is particularly beneficial for couples facing male infertility issues, such as low sperm count or poor sperm motility. The precision of ICSI allows for a more targeted approach to fertilization, which can be crucial in cases where traditional insemination methods have failed.
ICSI has significantly elevated success rates for male infertility, making it a popular choice within ART and drastically increasing the odds of conception when conventional methods are less effective. Moreover, the procedure has opened doors for men who may have previously felt hopeless about their fertility issues, allowing them to actively participate in the conception process. As research continues to evolve, ICSI techniques are becoming even more refined, further enhancing the prospects for couples seeking to overcome infertility challenges.
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT) and Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT) and Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT) are less common but important ART techniques. GIFT involves placing both eggs and sperm directly into the fallopian tubes, allowing fertilization to occur naturally. This method can be suitable for women with healthy fallopian tubes who prefer a less invasive approach. GIFT may also appeal to couples who desire a more natural conception experience, as it mimics the body's reproductive processes.
ZIFT, on the other hand, involves transferring a fertilized egg (zygote) into the fallopian tubes after fertilization. Both techniques seek to enhance the natural process of conception while leveraging full laboratory control over the gametes involved. These methods can be particularly beneficial for women with certain medical conditions that may impede traditional IVF success, offering alternative pathways to achieving pregnancy. As ART continues to advance, GIFT and ZIFT remain vital options in the diverse landscape of reproductive technologies, providing hope and solutions for those facing infertility.
Surgical Treatments for Infertility
In certain cases, surgery may be necessary to treat infertility. Surgical interventions can correct anatomical issues or remove obstructions that prevent conception.
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are minimally invasive surgical techniques used to examine and treat reproductive organs. Laparoscopy allows doctors to view the abdominal cavity, assessing for conditions such as endometriosis or pelvic adhesions, which can interfere with fertility.
Hysteroscopy is utilized to inspect the uterine cavity, diagnosing and treating conditions like fibroids or polyps that may impede implantation. Both procedures have improved the understanding of infertility and provided solutions for many couples seeking to conceive. These techniques not only offer a clearer picture of the reproductive anatomy but also allow for immediate intervention, often leading to quicker recovery times and less postoperative discomfort compared to traditional open surgeries. The ability to perform these procedures on an outpatient basis means that many patients can return home the same day, making them a convenient option for those navigating the complexities of infertility.
Tubal Surgeries
Tubal surgeries aim to address blockages or damage in the fallopian tubes, which are critical for natural conception. Conditions such as ectopic pregnancy or pelvic inflammatory disease can result in tubal damage, necessitating surgical intervention.
Through procedures such as salpingostomy or fimbrioplasty, healthcare providers can enhance the function of the fallopian tubes, significantly improving the chances of achieving pregnancy naturally. The success rates of these surgeries can vary based on the extent of the damage and the woman's age, but many women have reported positive outcomes following these interventions. Additionally, advancements in surgical techniques and technology have led to improved precision and outcomes, allowing for more effective restoration of tubal patency and function.
Treatment for Male Infertility
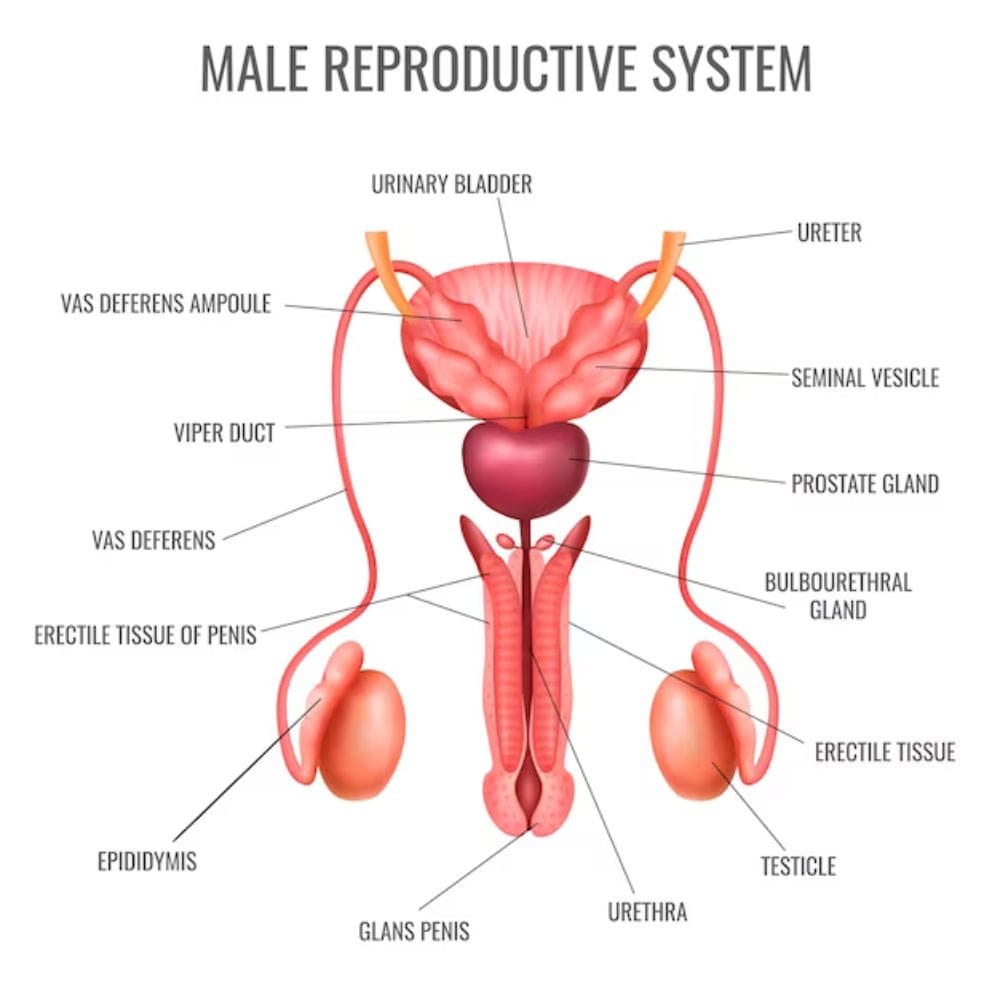
Addressing male infertility often requires a multi-faceted approach, depending on the underlying issues. Surgical options of necessity may include varicocelectomy (removal of swollen veins in the scrotum) or epididymal sperm aspiration to retrieve sperm directly for use in ART.
These surgical methods can bypass the conventional route of sperm production and improve reproductive health, allowing for successful conception through assisted reproductive technologies if necessary. Furthermore, the psychological impact of male infertility should not be overlooked, as men may experience feelings of inadequacy or stress related to their fertility challenges. Support groups and counseling can be invaluable resources for men undergoing these procedures, helping them navigate their emotions and fostering a sense of community during a challenging time.
In conclusion, the landscape of infertility treatment continues to evolve, offering hope and solutions for couples struggling to conceive. By understanding the causes, exploring hormonal options, leveraging assisted technologies, and considering surgical interventions, individuals and couples can embark on their journey toward parenthood with informed choices and support.
Thanks for reading.
BestPharmaReviews.